- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录1902 > AT32UC3C2512C-A2UT (Atmel)IC MCU AVR32 512K FLASH 64TQFP
90
32117DS–AVR-01/12
AT32UC3C
8.
Mechanical Characteristics
8.1
Thermal Considerations
8.1.1
Thermal Data
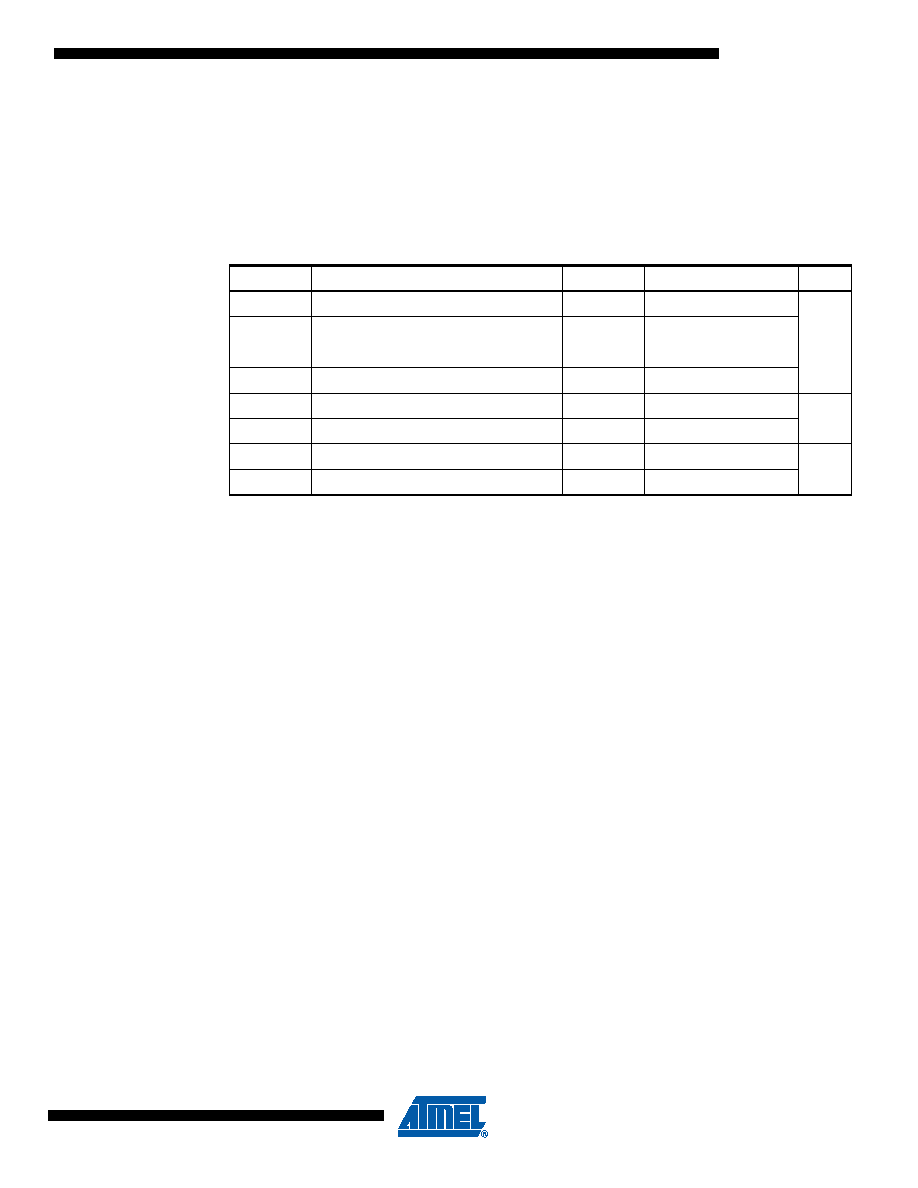
Table 8-1 summarizes the thermal resistance data depending on the package.
8.1.2
Junction Temperature
The average chip-junction temperature, T
J, in °C can be obtained from the following:
1.
2.
where:
θ
JA = package thermal resistance, Junction-to-ambient (°C/W), provided in Table 8-1 on page
θ
JC = package thermal resistance, Junction-to-case thermal resistance (°C/W), provided in
θ
HEAT SINK = cooling device thermal resistance (°C/W), provided in the device datasheet.
P
D = device power consumption (W) estimated from data provided in the section ”Power
T
A = ambient temperature (°C).
From the first equation, the user can derive the estimated lifetime of the chip and decide if a
cooling device is necessary or not. If a cooling device is to be fitted on the chip, the second
equation should be used to compute the resulting average chip-junction temperature T
J in °C.
Table 8-1.
Thermal Resistance Data
Symbol
Parameter
Condition
Package
Typ
Unit
θ
JA
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance
No air flow
QFN64
20.0
°C/W
θ
JC
Junction-to-case thermal resistance
QFN64
0.8
θ
JA
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance
No air flow
TQFP64
40.5
°C/W
θ
JC
Junction-to-case thermal resistance
TQFP64
8.7
θ
JA
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance
No air flow
TQFP100
39.3
°C/W
θ
JC
Junction-to-case thermal resistance
TQFP100
8.5
θ
JA
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance
No air flow
LQFP144
38.1
°C/W
θ
JC
Junction-to-case thermal resistance
LQFP144
8.4
TJ
TA
PD θJA
×
()
+
=
TJ
TA
P
(
D
θ
(
HEATSINK
×θ
JC ))
++
=
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
AT32UC3C2512C-A2ZT
IC MCU 32BIT 512KB FLASH 64TQFP
AT32UC3L016-D3HR
MCU AVR32 16K FLASH 48TTLGA
AT42QT5480-CU QS444
IC SENSOR DUAL TOUCH 49-BGA
AT6010H-4QI
IC FPGA 4NS 240PQFP
AT80C31X2-SLRUM
MCU ROMLESS 31X2 5V 44-PLCC
AT80C51RD2-SLRUM
IC MCU 80C51 HI PERFORM 44PLCC
AT85C51SND3B1-RTTUL
IC DECODER/ENCODER DGTL 100-LQFP
AT87251G2D-RLTUM
IC MCU 8/16BIT 32K OTP 44-VQFP
相关代理商/技术参数
AT32UC3C2512C-A2ZR
功能描述:32位微控制器 - MCU 512KB FL,-40/125oC AUTO
RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:C28x 处理器系列:TMS320F28x 数据总线宽度:32 bit 最大时钟频率:90 MHz 程序存储器大小:64 KB 数据 RAM 大小:26 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2.97 V to 3.63 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:LQFP-80 安装风格:SMD/SMT
AT32UC3C2512C-A2ZT
功能描述:32位微控制器 - MCU 512KB FL,-40/125oC AUTO
RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:C28x 处理器系列:TMS320F28x 数据总线宽度:32 bit 最大时钟频率:90 MHz 程序存储器大小:64 KB 数据 RAM 大小:26 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2.97 V to 3.63 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:LQFP-80 安装风格:SMD/SMT
AT32UC3C2512C-Z2UR
制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:MCU 32-bit AT32 AVR RISC 512KB Flash 3.3V/5V 64-Pin QFN EP T/R 制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:512KB FLASH 64QFN(-40?C TO 85?C) T&R - Tape and Reel 制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:IC MCU 32BIT 512KB FLASH 64QFN 制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:32-bit Microcontrollers - MCU 512KB Flash 64QFN (-40oC to 85oC) 制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:512KB Flash 64QFN(-40C to 85C) T&R
AT32UC3C2512C-Z2UT
制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:512KFLASH AUTO - Trays
AT32UC3C2512C-Z2ZES
制造商:Atmel Corporation 功能描述:512KFLASH UC3C AUTO - QFN64 ENG SAMPLE - Bulk
AT32UC3C2512C-Z2ZR
功能描述:32位微控制器 - MCU 512KB FL,-40/125oC AUTO
RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:C28x 处理器系列:TMS320F28x 数据总线宽度:32 bit 最大时钟频率:90 MHz 程序存储器大小:64 KB 数据 RAM 大小:26 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2.97 V to 3.63 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:LQFP-80 安装风格:SMD/SMT
AT32UC3C2512C-Z2ZT
功能描述:32位微控制器 - MCU 512KB FL,-40/125oC AUTO
RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:C28x 处理器系列:TMS320F28x 数据总线宽度:32 bit 最大时钟频率:90 MHz 程序存储器大小:64 KB 数据 RAM 大小:26 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2.97 V to 3.63 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:LQFP-80 安装风格:SMD/SMT
AT32UC3C264C-A2UR
功能描述:32位微控制器 - MCU UC3C 64K FLASH 16K SRAM
RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:C28x 处理器系列:TMS320F28x 数据总线宽度:32 bit 最大时钟频率:90 MHz 程序存储器大小:64 KB 数据 RAM 大小:26 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2.97 V to 3.63 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:LQFP-80 安装风格:SMD/SMT